International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River: Difference between revisions
Wavelength (talk | contribs) revising letter case—MOS:HEAD |
Moscow Mule (talk | contribs) |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 26 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|International environmental organisation}} |
|||
__NOTOC__ |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=November 2019}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{unreferenced|date=August 2019}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
The '''International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River''' ('''ICPDR''') is an international organisation with its permanent secretariat in [[Vienna]]. It was established by the Danube River Protection Convention, signed by the Danube countries in [[Sofia]], [[Bulgaria]], in 1994. |
The '''International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River''' ('''ICPDR''') is an international organisation with its permanent secretariat in [[Vienna]]. It was established by the Danube River Protection Convention, signed by the [[Danube]] countries in [[Sofia]], [[Bulgaria]], in 1994. |
||
The TransNational Monitoring Network (TNMN) began in 1996, and the Accident Emergency Warning System (AEWS) first came into operation in 1997 – both continue today as key transnational measures under the ICPDR. Although the ICPDR contracting parties are a mix of EU Member States and Non-Member States, all have committed themselves to meeting the requirements of the EU [[Water Framework Directive]]. This commitment was augmented by the EU Floods Directive in 2007. The ICPDR celebrated 25 years of the Danube River Protection Convention in 2019. |
|||
The commission became active in 1998. Since then, it has grown into one of the largest and most active international bodies of [[Drainage basin|river basin]] management expertise in Europe. The commission deals not only with the [[Danube]] itself, but also with the whole Danube [[River Basin]], which includes more than 300 tributaries and the [[Groundwater|ground water]] resources. |
|||
==Legal basis== |
==Legal basis== |
||
| ⚫ | The ICPDR’s legal basis is the Convention on Cooperation for the Protection and Sustainable use of the Danube River, generally referred to as the Danube River Protection Convention or DRPC. It commits the contracting parties to join their efforts in sustainable water management, including conservation of surface and [[ground water]], [[pollution]] reduction, and the prevention and control of floods, accidents and ice hazards. The convention was signed in Sofia, Bulgaria, in 1994 and came into force in October 1998. |
||
| ⚫ | The ICPDR’s legal basis is the |
||
==Objectives== |
==Objectives== |
||
The ICPDR was created to implement the Danube River Protection Convention (DRPC). It is both a forum to allow its contracting parties to coordinate the implementation of the convention and a platform to review the progress they make. The key objectives of the ICPDR include the following: |
The ICPDR was created to implement the Danube River Protection Convention (DRPC). It is both a forum to allow its contracting parties to coordinate the implementation of the convention and a platform to review the progress they make. The key objectives of the ICPDR include the following: |
||
# Ensure sustainable water management |
# Ensure sustainable water management |
||
# Ensure conservation, improvement and rational use of surface waters and ground water |
|||
# Control pollution and reduce inputs of nutrients and hazardous substances |
# Control pollution and reduce inputs of nutrients and hazardous substances |
||
# Control floods and ice hazards |
# Control floods and ice hazards |
||
The ICPDR |
The ICPDR facilitates cooperation between the Danube countries and the [[Black Sea]] region in issues requiring coordination. It cooperates with other international organisations where appropriate to address new challenges related to water management as they emerge. As of its adoption in 2000, a commitment to implementing the EU’s [[Water Framework Directive]] (WFD, formally Directive 2000/60/EC) is also central to the activities of all ICPDR members, including non-EU members. |
||
When the |
When the Water Framework Directive was adopted in October 2000, all countries cooperating under the DRPC (which includes at present 9 EU and 5 non EU member states) nominated the ICPDR as the platform for the Implementation of all transboundary aspects of the EU Water Framework Directive. They decided to make all efforts to implement the Directive throughout the whole basin. The Non EU Member States also committed themselves to implement the WFD within the frame of the DRPC. In addition, the ICPDR serves as a coordination platform for the basin-wide implementation of the EU [[Floods directive]] (EFD, formally Directive 2007/60/EC). |
||
==Structure and decision making== |
==Structure and decision making== |
||
| ⚫ | The ICPDR is an international organisation. It meets twice a year: The Ordinary Meeting is held in [[Vienna]] in December, another meeting of Heads of Delegations, the Standing Working Group, is held in June in the country of the Presidency. The meetings consist of delegations of contracting parties and observer organisations. Every contracting party has one Head of Delegation representing the country. For all decisions the achievement of consensus is sought. The meetings are chaired by the ICPDR President; ICPDR Presidency is passed on from one country to another in an alphabetical order every year. |
||
| ⚫ | Much of the work of the ICPDR is done by Expert Groups (EGs), which are panels of specialists from the ICPDR contracting parties and observers – usually civil servants of the relevant ministries, in some cases employees of NGOs or contracted agencies. There are seven permanent Expert Groups and one ad hoc Expert Group as of 2020: |
||
| ⚫ | The ICPDR is an international organisation. It meets twice a year: The Ordinary Meeting is held in [[Vienna]] in December, another meeting of Heads of Delegations is held in June in the country of the Presidency. The meetings consist of delegations of contracting parties and observer organisations. Every contracting party has one Head of Delegation representing the country. For all decisions the achievement of consensus is sought. The meetings are chaired by the ICPDR President; ICPDR Presidency is passed on from one country to another in an alphabetical order every year. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
# Pressures and Measures |
# Pressures and Measures |
||
| Line 40: | Line 38: | ||
The expert groups all have Terms of Reference and mandates adopted by the Commission. They usually meet twice to three times a year. Time- and target-limited task groups may also be established for specific tasks which not necessarily all countries are represented in. The expert groups discuss issues related to their Terms of Reference and prepare reports and recommendations for coordinated action. |
The expert groups all have Terms of Reference and mandates adopted by the Commission. They usually meet twice to three times a year. Time- and target-limited task groups may also be established for specific tasks which not necessarily all countries are represented in. The expert groups discuss issues related to their Terms of Reference and prepare reports and recommendations for coordinated action. |
||
The ICPDR has a Permanent Secretariat to support its work, supervised by an Executive Secretary, as of 2013, [[Ivan Zavadsky]]. The secretariat has its headquarters in Vienna, from where it administers, manages and supports the work of the ICPDR. The total staff of the secretariat is |
The ICPDR has a Permanent Secretariat to support its work, supervised by an Executive Secretary, as of 2013, [[Ivan Zavadsky]]. The secretariat has its headquarters in Vienna, from where it administers, manages and supports the work of the ICPDR. The total staff of the secretariat is 9 permanent staff members and additional short-term project staff. If all national experts, delegates from observers and consultants are considered, there are more than 300 people working with and for the ICPDR. |
||
== |
==Regular activities== |
||
On 29 June each year, the 14 countries of the Danube River Basin jointly acknowledge [http://www.danubeday.at/ Danube Day], a day celebrating their shared river system with a series of live events at schools and other public buildings. Largely targeting youth and education, the day includes challenges, quizzes, teaching events, folk dancing, traditional music, and similar activities shared throughout the region. The first Danube Day was held on the 10th anniversary of the signing of the Danube River Protection Convention in 2004. |
|||
Also held since 2004, the ICPDR also co-runs [http://www.danubeday.org/Danube_Art_Master Danube Art Master] with the Global Water Partnership Central and Eastern Europe (GWP CEE). An art competition involving thousands of school pupils throughout the Danube River Basin, DAM invites pupils to create original artworks, with winners chosen every year by a panel of judges. |
|||
| ⚫ | The ICPDR serves as a platform for |
||
==Dispute prevention and resolution== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The ICPDR serves as a platform for cooperation and coordination . The signing of the Convention, however, commits the countries under international law to some specific actions and to uphold certain principles. In some past disputes, the ICPDR was able to contribute towards the harmonisation of efforts by providing a platform for discussion. |
||
The Convention provides a dispute settlement mechanism, but in practice this has not been necessary thus far, as the countries concerned have worked to ensure dialogue and developed consensus on issues of conflict. The work of the ICPDR is less prone to disputes than outsiders might imagine. The atmosphere at meetings is focused on facts and characterised by mutual respect and a common acknowledgement of the ICPDR’s objectives and tasks. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
The ICPDR has fifteen contracting parties: |
The ICPDR has fifteen contracting parties: |
||
{{div col| |
{{div col|colwidth=30em}} |
||
* {{AUT}} |
* {{AUT}} |
||
* {{BIH}} |
* {{BIH}} |
||
| Line 71: | Line 74: | ||
==Observers== |
==Observers== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Black Sea#The Commission on the Protection of the Black Sea Against Pollution|Black Sea Commission]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Black_Sea#The_Commission_on_the_Protection_of_the_Black_Sea_Against_Pollution|Black Sea Commission]] |
|||
* [[Carpathian Convention]] |
* [[Carpathian Convention]] |
||
* [[Central Dredging Association]] |
* [[Central Dredging Association]] |
||
* [ |
* [https://www.eip-water.eu/organisations/def-%E2%80%93-danube-environmental-forum Danube Environmental Forum] |
||
* [[Danube Commission]] |
* [[Danube Commission]] |
||
* [https://dcsf.danubestrategy.eu/ Danube Civil Society Forum] |
|||
* [[Danube Parks]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Danube Tourist Commission]] |
|||
* [http://www.danubeparks.org/ Danube Parks] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* [http://www.dstf.eu/species/acipenser-sturio/ Danube Sturgeon Task Force] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150630163432/http://www.dstf.eu/species/acipenser-sturio/ |date=30 June 2015 }} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* [https://dlap.danubestrategy.eu/organisations/danube-tourist-commission-0 Danube Tourist Commission] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* |
* [https://www.danube-iad.eu/ International Association for Danube Research] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[VGB PowerTech]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* |
|||
* [[via donau]] |
* [[via donau]] |
||
* [[World Wide Fund for Nature]] — |
* [[World Wide Fund for Nature]] — Central Eastern Europe |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{div col end}} |
{{div col end}} |
||
==Funding== |
==Funding== |
||
The ICPDR budget comes from the contributions of the Contracting Parties. According to the Danube River Protection Convention, the Contracting Parties (except for the EU) shall contribute an equal share, unless unanimously decided otherwise by the ICPDR. Some exceptions are currently applied for a transitional period. The total annual budget of the ICPDR is a little more than one million Euros. Much of the |
The ICPDR budget comes from the contributions of the Contracting Parties. According to the Danube River Protection Convention, the Contracting Parties (except for the EU) shall contribute an equal share, unless unanimously decided otherwise by the ICPDR. Some exceptions are currently applied for a transitional period. The total annual budget of the ICPDR is a little more than one million Euros. Much of the ICPDR's work is done directly by Member Countries. Such contributions in staff and material are therefore also considerable, even though this does not show in the ICPDR budget. Costs of participation in the Commission's and Expert bodies’ work are also covered by the parties themselves. |
||
In some cases, the ICPDR engages in projects that have separate sources of funding. These include projects funded by the European Union, the [[United Nations Development |
In some cases, the ICPDR engages in projects that have separate sources of funding. These include projects funded by the European Union, the [[United Nations Development Programme]], GEF, and individual countries. |
||
==Danube River variety== |
==Danube River variety== |
||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:Donaueschingen Donauzusammenfluss 20080714.jpg|The place where Breg and Brigach unite to form the Danube in [[Donaueschingen]]. |
File:Donaueschingen Donauzusammenfluss 20080714.jpg|The place where Breg and Brigach unite to form the Danube in [[Donaueschingen]]. |
||
| Line 112: | Line 115: | ||
File:DonauknieVisegrad.jpg|The Danube Bend is a curve of the Danube in [[Geography of Hungary|Hungary]], near the city of [[Visegrád]]. |
File:DonauknieVisegrad.jpg|The Danube Bend is a curve of the Danube in [[Geography of Hungary|Hungary]], near the city of [[Visegrád]]. |
||
File:Parliament Budapest Hungary.jpg|The Danube in [[Budapest]] |
File:Parliament Budapest Hungary.jpg|The Danube in [[Budapest]] |
||
File:Tvdjava iz vazduha.jpg|Confluence of [[Sava]] into Danube in [[Belgrade]], [[Serbia]] |
|||
File:Pelicani din Delta Dunarii.PNG|[[Pelicans]] in the Danube Delta, Romania |
File:Pelicani din Delta Dunarii.PNG|[[Pelicans]] in the Danube Delta, Romania |
||
| Line 119: | Line 122: | ||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
*[[Internationalization of the Danube River]], for events from earliest times to the Treaty of Paris in 1856 |
*[[Internationalization of the Danube River]], for events from earliest times to the Treaty of Paris in 1856 |
||
*[[Commissions of the Danube River]], for the international |
*[[Commissions of the Danube River]], for the international bodies governing the waterway from 1856 to 1940 |
||
*[[Danube River Conference of 1948]] |
*[[Danube River Conference of 1948]] |
||
*[[Danube Commission]], for the international agency charged with transportation oversight of the river |
*[[Danube Commission]], for the international agency charged with transportation oversight of the river |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* {{Official website|http://www.icpdr.org}} |
|||
* [http://www.icpdr.org Official site of the International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River] |
|||
* [http://www.icpdr.org/icpdr-pages/drpc.htm Danube River Protection Convention] |
** [http://www.icpdr.org/icpdr-pages/drpc.htm Danube River Protection Convention] |
||
* [https://www.icpdr.org/main/publications/convention-action-25-years-icpdr From Convention to Action: 25 Years of the ICPDR] |
|||
* [http://www.europarl.europa.eu/sides/getDoc.do?pubRef=-//EP//TEXT+TA+P7-TA-2011-0065+0+DOC+XML+V0//EN&language=EN ''Implementation of the EU Strategy for the Danube Region,'' European Union, 17 February 2011] |
* [http://www.europarl.europa.eu/sides/getDoc.do?pubRef=-//EP//TEXT+TA+P7-TA-2011-0065+0+DOC+XML+V0//EN&language=EN ''Implementation of the EU Strategy for the Danube Region,'' European Union, 17 February 2011] |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Organizations established in 1998]] |
|||
[[Category:Danube]] |
[[Category:Danube]] |
||
[[Category:Environmental agencies]] |
|||
[[Category:Environmental protection]] |
[[Category:Environmental protection]] |
||
[[Category:Intergovernmental organizations established by treaty]] |
[[Category:Intergovernmental organizations established by treaty]] |
||
[[Category:Environmental |
[[Category:Environmental organizations established in 1994]] |
||
[[Category:1994 establishments in Europe]] |
|||
[[Category:1994 establishments in the European Union]]<!--member--> |
|||
Latest revision as of 03:41, 14 May 2024
The International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River (ICPDR) is an international organisation with its permanent secretariat in Vienna. It was established by the Danube River Protection Convention, signed by the Danube countries in Sofia, Bulgaria, in 1994.
The TransNational Monitoring Network (TNMN) began in 1996, and the Accident Emergency Warning System (AEWS) first came into operation in 1997 – both continue today as key transnational measures under the ICPDR. Although the ICPDR contracting parties are a mix of EU Member States and Non-Member States, all have committed themselves to meeting the requirements of the EU Water Framework Directive. This commitment was augmented by the EU Floods Directive in 2007. The ICPDR celebrated 25 years of the Danube River Protection Convention in 2019.
Legal basis[edit]
The ICPDR’s legal basis is the Convention on Cooperation for the Protection and Sustainable use of the Danube River, generally referred to as the Danube River Protection Convention or DRPC. It commits the contracting parties to join their efforts in sustainable water management, including conservation of surface and ground water, pollution reduction, and the prevention and control of floods, accidents and ice hazards. The convention was signed in Sofia, Bulgaria, in 1994 and came into force in October 1998.
Objectives[edit]
The ICPDR was created to implement the Danube River Protection Convention (DRPC). It is both a forum to allow its contracting parties to coordinate the implementation of the convention and a platform to review the progress they make. The key objectives of the ICPDR include the following:
- Ensure sustainable water management
- Control pollution and reduce inputs of nutrients and hazardous substances
- Control floods and ice hazards
The ICPDR facilitates cooperation between the Danube countries and the Black Sea region in issues requiring coordination. It cooperates with other international organisations where appropriate to address new challenges related to water management as they emerge. As of its adoption in 2000, a commitment to implementing the EU’s Water Framework Directive (WFD, formally Directive 2000/60/EC) is also central to the activities of all ICPDR members, including non-EU members.
When the Water Framework Directive was adopted in October 2000, all countries cooperating under the DRPC (which includes at present 9 EU and 5 non EU member states) nominated the ICPDR as the platform for the Implementation of all transboundary aspects of the EU Water Framework Directive. They decided to make all efforts to implement the Directive throughout the whole basin. The Non EU Member States also committed themselves to implement the WFD within the frame of the DRPC. In addition, the ICPDR serves as a coordination platform for the basin-wide implementation of the EU Floods directive (EFD, formally Directive 2007/60/EC).
Structure and decision making[edit]
The ICPDR is an international organisation. It meets twice a year: The Ordinary Meeting is held in Vienna in December, another meeting of Heads of Delegations, the Standing Working Group, is held in June in the country of the Presidency. The meetings consist of delegations of contracting parties and observer organisations. Every contracting party has one Head of Delegation representing the country. For all decisions the achievement of consensus is sought. The meetings are chaired by the ICPDR President; ICPDR Presidency is passed on from one country to another in an alphabetical order every year.
Much of the work of the ICPDR is done by Expert Groups (EGs), which are panels of specialists from the ICPDR contracting parties and observers – usually civil servants of the relevant ministries, in some cases employees of NGOs or contracted agencies. There are seven permanent Expert Groups and one ad hoc Expert Group as of 2020:
- Pressures and Measures
- Monitoring and Assessment
- Flood Protection
- River Basin Management
- Information Management and GIS
- Public Participation and Communication
- Accident Prevention and Control
- Strategic Expert Group (ad hoc)
The expert groups all have Terms of Reference and mandates adopted by the Commission. They usually meet twice to three times a year. Time- and target-limited task groups may also be established for specific tasks which not necessarily all countries are represented in. The expert groups discuss issues related to their Terms of Reference and prepare reports and recommendations for coordinated action.
The ICPDR has a Permanent Secretariat to support its work, supervised by an Executive Secretary, as of 2013, Ivan Zavadsky. The secretariat has its headquarters in Vienna, from where it administers, manages and supports the work of the ICPDR. The total staff of the secretariat is 9 permanent staff members and additional short-term project staff. If all national experts, delegates from observers and consultants are considered, there are more than 300 people working with and for the ICPDR.
Regular activities[edit]
On 29 June each year, the 14 countries of the Danube River Basin jointly acknowledge Danube Day, a day celebrating their shared river system with a series of live events at schools and other public buildings. Largely targeting youth and education, the day includes challenges, quizzes, teaching events, folk dancing, traditional music, and similar activities shared throughout the region. The first Danube Day was held on the 10th anniversary of the signing of the Danube River Protection Convention in 2004.
Also held since 2004, the ICPDR also co-runs Danube Art Master with the Global Water Partnership Central and Eastern Europe (GWP CEE). An art competition involving thousands of school pupils throughout the Danube River Basin, DAM invites pupils to create original artworks, with winners chosen every year by a panel of judges.
Dispute prevention and resolution[edit]
The ICPDR serves as a platform for cooperation and coordination . The signing of the Convention, however, commits the countries under international law to some specific actions and to uphold certain principles. In some past disputes, the ICPDR was able to contribute towards the harmonisation of efforts by providing a platform for discussion.
The Convention provides a dispute settlement mechanism, but in practice this has not been necessary thus far, as the countries concerned have worked to ensure dialogue and developed consensus on issues of conflict. The work of the ICPDR is less prone to disputes than outsiders might imagine. The atmosphere at meetings is focused on facts and characterised by mutual respect and a common acknowledgement of the ICPDR’s objectives and tasks.
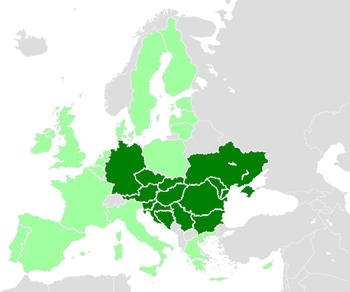
Members[edit]

is the catchment area of the river.
The ICPDR has fifteen contracting parties:
Observers[edit]
The ICPDR has 24 official observers with rights to attend meetings and participate in decision-making:
- Black Sea Commission
- Carpathian Convention
- Central Dredging Association
- Danube Environmental Forum
- Danube Commission
- Danube Civil Society Forum
- Danube Competence Center
- Danube Parks
- Danube Sturgeon Task Force Archived 30 June 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- Danube Tourist Commission
- European Anglers Alliance
- European Barge Union
- European Water Association
- Friends of Nature International
- Global Water Partnership
- International Association for Danube Research
- International Association of Water Supply Companies in the Danube River Catchment Area
- International Hydrological Programme
- International Sava River Basin Commission
- Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
- Regional Environmental Center for Central and Eastern Europe
- via donau
- World Wide Fund for Nature — Central Eastern Europe
Funding[edit]
The ICPDR budget comes from the contributions of the Contracting Parties. According to the Danube River Protection Convention, the Contracting Parties (except for the EU) shall contribute an equal share, unless unanimously decided otherwise by the ICPDR. Some exceptions are currently applied for a transitional period. The total annual budget of the ICPDR is a little more than one million Euros. Much of the ICPDR's work is done directly by Member Countries. Such contributions in staff and material are therefore also considerable, even though this does not show in the ICPDR budget. Costs of participation in the Commission's and Expert bodies’ work are also covered by the parties themselves.
In some cases, the ICPDR engages in projects that have separate sources of funding. These include projects funded by the European Union, the United Nations Development Programme, GEF, and individual countries.
Danube River variety[edit]
-
The place where Breg and Brigach unite to form the Danube in Donaueschingen.
-
The Danube in Ulm as seen from the steeple of Ulm Minster, looking southwest.
-
The Vienna International Centre, home of the ICPDR's permanent secretariat
-
The Danube in Budapest
-
Pelicans in the Danube Delta, Romania
See also[edit]
- Internationalization of the Danube River, for events from earliest times to the Treaty of Paris in 1856
- Commissions of the Danube River, for the international bodies governing the waterway from 1856 to 1940
- Danube River Conference of 1948
- Danube Commission, for the international agency charged with transportation oversight of the river







