Lockheed C-121 Constellation: Difference between revisions
→Variants: avoid redirect; use 'Main' |
No edit summary |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 27 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Military transport version of Constellation}} |
|||
{|{{Infobox aircraft begin |
{|{{Infobox aircraft begin |
||
|name = C-121/R7O/R7V <br>Constellation |
|name = C-121/R7O/R7V <br>Constellation |
||
|image = Lockheed C-121G-LO 54-4052 1501st Air Transport Group over Golden Gate Bridge.jpg |
|image = File:Lockheed C-121G-LO 54-4052 1501st Air Transport Group over Golden Gate Bridge.jpg |
||
|size = 300px |
|||
|alt = A MATS C-121G Super Constellation flying near the Golden Gate Bridge. |
|alt = A MATS C-121G Super Constellation flying near the Golden Gate Bridge. |
||
|caption = A [[Military Air Transport Service]] C-121G Super Constellation flying near the Golden Gate Bridge. |
|caption = A [[Military Air Transport Service]] C-121G Super Constellation flying near the Golden Gate Bridge. |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
}}{{Infobox aircraft type |
}}{{Infobox aircraft type |
||
|type = Military transport |
|type = Military transport |
||
|national origin = |
|national origin = United States |
||
|manufacturer = [[Lockheed Corporation |
|manufacturer = [[Lockheed Corporation]] |
||
|designer = |
|designer = |
||
|first flight = March 14, 1947 |
|first flight = March 14, 1947 |
||
|introduction = November 12, 1948 |
|introduction = November 12, 1948 |
||
|retired = |
|retired = |
||
|status = Retired, two |
|status = Retired from military service, two operated by civilian preservation organisations |
||
|primary user = [[United States Air Force]] <br>[[United States Navy]] |
|primary user = [[United States Air Force]] <br>[[United States Navy]] |
||
|more users = |
|more users = |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
|} |
|} |
||
The '''Lockheed C-121 Constellation''' is a military transport version of the [[Lockheed Constellation]]. A total of 332 aircraft were constructed for both the [[United States Air Force]] and [[United States Navy]] for various purposes. Numerous [[Lockheed EC-121 Warning Star|airborne early warning versions]] were also constructed. The C-121 later saw service with smaller civilian operators until 1993. |
|||
The '''Lockheed C-121 Constellation''' was a military transport version of the [[Lockheed Constellation]]. A total of 332 aircraft were constructed for both the [[United States Air Force]] and [[United States Navy]] for various purposes. Numerous [[Lockheed EC-121 Warning Star|AWACS versions]] were also constructed. The C-121 later saw service with smaller civilian operators until 1993. |
|||
==Design and development== |
==Design and development== |
||
| Line 34: | Line 33: | ||
In 1947, Lockheed unveiled a more economical Constellation. The [[L-749]] as it was known, had extra fuel capacity and a more economical version of the R-3350. However, Lockheed had lost 1200 workers that same year. By 1948, production of the L-749 was at a near halt. It was then that the [[United States Air Force]] (USAF) signed a contract with Lockheed for ten L-749A aircraft designated the C-121A. The [[United States Navy]] (USN) had also placed an order for two AWACS versions of the L-749A designated the [[Lockheed EC-121 Warning Star|PO-1W]] (later WV-1). The first L-749A variants off the production line were for the US military. |
In 1947, Lockheed unveiled a more economical Constellation. The [[L-749]] as it was known, had extra fuel capacity and a more economical version of the R-3350. However, Lockheed had lost 1200 workers that same year. By 1948, production of the L-749 was at a near halt. It was then that the [[United States Air Force]] (USAF) signed a contract with Lockheed for ten L-749A aircraft designated the C-121A. The [[United States Navy]] (USN) had also placed an order for two AWACS versions of the L-749A designated the [[Lockheed EC-121 Warning Star|PO-1W]] (later WV-1). The first L-749A variants off the production line were for the US military. |
||
The C-121A versions differed from the L-749 only through having a reinforced floor to handle cargo, and a large aft loading door. Although originally intended for cargo transport duties, they were usually fitted out with 44-seat passenger transport interiors. The aircraft also consisted of a five |
The C-121A versions differed from the L-749 only through having a reinforced floor to handle cargo, and a large aft loading door. Although originally intended for cargo transport duties, they were usually fitted out with 44-seat passenger transport interiors. The aircraft also consisted of a five-man crew with four relief crew members on standby. All C-121As were assigned to the Atlantic division of the [[Military Air Transport Service]] (MATS). The aircraft would later see service in the [[Berlin Airlift]]. [[Dwight Eisenhower]] and [[General Douglas MacArthur]] both used the C-121A as their personal VIP transports. In 1950, six of the C-121A Constellations were modified as VIP transports and redesignated VC-121A. The last C-121As were retired in 1968. |
||
In August 1950, the USN ordered eleven passenger/cargo convertible versions of Lockheed's stretched L-1049B Super Constellation (which it had already ordered as the WV-2 AWACS platform). These aircraft, originally designated R7O, were delivered before the WV-2 aircraft due to the R7O being more simple to produce. The R7O (now R7V-1) first flew in 1952. The R7V-1 was able to be quickly converted between a passenger transport for 97-107 individuals or a cargo carrying transport in two hours. The Navy reduced the number of available seats to fit room for life rafts on overseas flights. 73 stretchers could also be used for medical evacuation flights. The R7V-1s saw service over the Atlantic and Pacific in squadrons VR-1 (the oldest transport squadron in the Navy), VR-7 and VR-8. Two modified R7V-1 aircraft were used on Antarctic supply missions while conducting tests and observations at the same time. One crashed on landing in 1970 and remains at the spot to the present day; the other was retired in 1971. In 1962, 32 of the 50 R7V-1 aircraft in Naval service were transferred to the Air Force, being re-designated the C-121G. The remaining 18 in Naval service were redesignated C-121J. One C-121J was later used by the [[Blue Angels]] until it was replaced by a [[Lockheed C-130 Hercules]] in 1971. |
In August 1950, the USN ordered eleven passenger/cargo convertible versions of Lockheed's stretched L-1049B Super Constellation (which it had already ordered as the WV-2 AWACS platform). These aircraft, originally designated R7O, were delivered before the WV-2 aircraft due to the R7O being more simple to produce. The R7O (now R7V-1) first flew in 1952. The R7V-1 was able to be quickly converted between a passenger transport for 97-107 individuals or a cargo carrying transport in two hours. The Navy reduced the number of available seats to fit room for life rafts on overseas flights. 73 stretchers could also be used for medical evacuation flights. The R7V-1s saw service over the Atlantic and Pacific in squadrons VR-1 (the oldest transport squadron in the Navy), VR-7 and VR-8. Two modified R7V-1 aircraft were used on Antarctic supply missions while conducting tests and observations at the same time. One crashed on landing in 1970 and remains at the spot to the present day; the other was retired in 1971. In 1962, 32 of the 50 R7V-1 aircraft in Naval service were transferred to the Air Force, being re-designated the C-121G. The remaining 18 in Naval service were redesignated C-121J. One C-121J was later used by the [[Blue Angels]] until it was replaced by a [[Lockheed C-130 Hercules]] in 1971. |
||
| Line 40: | Line 39: | ||
[[File:Lockheed Super Constellation "Southern Preservation" (VH-EAG) at Illawarra Regional Airport.jpg|thumb|The former USAF 54-0154, a C-121C operated by the Historical Aircraft Restoration Society fitted with non-standard wingtip fuel tanks, starts one of its engines]] |
[[File:Lockheed Super Constellation "Southern Preservation" (VH-EAG) at Illawarra Regional Airport.jpg|thumb|The former USAF 54-0154, a C-121C operated by the Historical Aircraft Restoration Society fitted with non-standard wingtip fuel tanks, starts one of its engines]] |
||
The USAF had also ordered 33 L-1049F Super Constellations in 1951, designated the C-121C. Unlike its Naval equivalent, the C-121C featured square cabin windows instead of round ones. Otherwise, the C-121C resembled the USN R7V-1 aircraft. The C-121C also featured a reinforced structure to handle turboprop engines if necessary. Other features of the C-121C included an [[Auxiliary Power Unit]] [[Turbo-compound]] R-3350s and the ability to carry 75 passengers, 72 fully equipped troops, or 47 stretchers. The seats could be stored under the floor of the aircraft when needed for cargo use. The first flight of a C-121C was in 1955. Deliveries began in August 1955, with aircraft being assigned to the MATS Atlantic division. The aircraft were later in service with the [[Air National Guard]] (ANG) and were retired in 1973. Four were later refitted as VC-121C VIP aircraft, six as EC-121S TV and radio broadcast relay systems, two became EC-121C Microwave Airborne Radio Communications (MARCOM) systems and one was converted to a DC-121C observation aircraft. |
The USAF had also ordered 33 L-1049F Super Constellations in 1951, designated the C-121C. Unlike its Naval equivalent, the C-121C featured square cabin windows instead of round ones. Otherwise, the C-121C resembled the USN R7V-1 aircraft. The C-121C also featured a reinforced structure to handle turboprop engines if necessary. Other features of the C-121C included an [[Auxiliary Power Unit]], [[Turbo-compound]] R-3350s, and the ability to carry 75 passengers, 72 fully equipped troops, or 47 stretchers. The seats could be stored under the floor of the aircraft when needed for cargo use. The first flight of a C-121C was in 1955. Deliveries began in August 1955, with aircraft being assigned to the MATS Atlantic division. The aircraft were later in service with the [[Air National Guard]] (ANG) and were retired in 1973. Four were later refitted as VC-121C VIP aircraft, six as EC-121S TV and radio broadcast relay systems, two became EC-121C Microwave Airborne Radio Communications (MARCOM) systems and one was converted to a DC-121C [[Surveillance aircraft|observation aircraft]]. |
||
[[File:Superconstellation movie. |
[[File:Superconstellation movie.ogv|thumb|left|A video of the Super Constellation Flyers Association's C-121C in flight.]] |
||
After military service, some C-121s and R7V-1s were used by civilian operators as cargo aircraft. The last operators were small [[Dominican Republic]] cargo airlines that operated to Miami with surplus military Constellations bought from [[Davis-Monthan Air Force Base]]. The operations stopped in 1993 after the [[Federal Aviation Administration]] (FAA) banned these operators from flying into the United States due to safety concerns. |
After military service, some C-121s and R7V-1s were used by civilian operators as cargo aircraft. The last operators were small [[Dominican Republic]] cargo airlines that operated to Miami with surplus military Constellations bought from [[Davis-Monthan Air Force Base]]. The operations stopped in 1993 after the [[Federal Aviation Administration]] (FAA) banned these operators from flying into the United States due to safety concerns. One former C-121Cs fly today with the Historical Aircraft Restoration Society of [[Australia]] and the other flew up to 2016 to Super Constellation Flyers Association of [[Switzerland]].<ref>[http://conniesurvivors.com/L1049.htm L1049 Super Constellation - Lockheed Constellation Survivors]; Petersen, Ralph M.; ''Retrieved 8/4/11''</ref><ref>Breffort, 2006, pp.146-159.</ref> The DIAG Aviation GmbH with the until 2016 flown exemplar is since then dismounted and put to be sold from 5 April 2023.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://aeroin.net/um-dos-dois-ultimos-lockheed-constellation-c-121c-do-mundo-pode-nunca-mais-voar/ | title=Um dos dois últimos Lockheed Constellation C-121C do mundo pode nunca mais voar | date=7 April 2023 }}</ref> |
||
{{Clear}} |
{{Clear}} |
||
==Variants== |
==Variants== |
||
{{Main|Lockheed Constellation variants}} |
{{Main article|Lockheed Constellation variants}} |
||
===Air Force=== |
===Air Force=== |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
:Four C-121J aircraft converted for VIP use. One operated with the [[Blue Angels]]. |
:Four C-121J aircraft converted for VIP use. One operated with the [[Blue Angels]]. |
||
<ref name="US Warplanes.net">[http://www.uswarplanes.net/c69c121.html C-69/C-121 - US Warplanes.net]; ''Retrieved 11/6/11''</ref><ref>Breffort, 2006, pp.166-169.</ref> |
<ref name="US Warplanes.net">[http://www.uswarplanes.net/c69c121.html C-69/C-121 - US Warplanes.net] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151026103610/http://www.uswarplanes.net/c69c121.html |date=2015-10-26 }}; ''Retrieved 11/6/11''</ref><ref>Breffort, 2006, pp.166-169.</ref> |
||
== Surviving aircraft == |
|||
==Specifications== |
|||
* N422NA - C-121A - Airworthy<ref>{{cite web |title=C-121A Constellation |url=https://lewisairlegends.com/lockheed-c121a-constellation-bataan |access-date=2023-05-08 |publisher=Lewis Air Legends}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Constellation Silh.jpg|thumb]] |
|||
* 54-0177 - C-121C on static display at the [[Smithsonian Institution]]'s [[Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center]] in [[Chantilly, Virginia]]<ref name="National Air and Space Museum 1943 i364">{{cite web | title=Lockheed 1049F-55-96, "Constellation" | website=National Air and Space Museum | date=1943-01-09 | url=https://airandspace.si.edu/collection-objects/lockheed-1049f-55-96-constellation/nasm_A19880371000 | access-date=2024-04-21}}</ref> |
|||
== |
==Specifications (C-121A / L-749A)== |
||
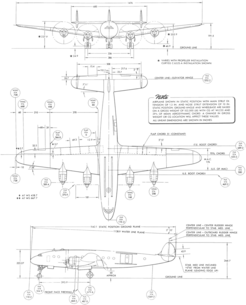
{{multiple image |
|||
{{aircraft specifications |
|||
|total_width = 500 |
|||
<!-- if you do not understand how to use this template, please ask at [[Wikipedia talk:WikiProject Aircraft]] --> |
|||
| image1 = Lockheed Model 649 Constellation 3-view line drawing.png |
|||
|plane or copter?=plane |
|||
| alt1 = 3-view line drawing of the Lockheed Model 649 Constellation |
|||
|jet or prop?=prop |
|||
| caption1 = 3-view line drawing of the Lockheed Model 649 Constellation |
|||
<!-- Now, fill out the specs. Please include units where appropriate (main comes first, alt in parentheses). If an item doesn't apply, like capacity, leave it blank. |
|||
| image2 = Lockheed C-121C Constellation 3-view line drawing.png |
|||
| alt2 = 3-view line drawing of the Lockheed C-121C Constellation |
|||
| caption2 = 3-view line drawing of the Lockheed C-121C Constellation |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Aircraft specs |
|||
--> |
|||
|ref= |
|ref=Lockheed Constellation:From Excalibur to Starliner,<ref>Breffort, 2006, p.175.</ref> Lockheed Constellation:From Excalibur to Starliner<ref>Breffort, 2006</ref> |
||
|prime units?=imp |
|||
<!-- |
<!-- |
||
General characteristics |
General characteristics |
||
| Line 107: | Line 113: | ||
|crew=5 |
|crew=5 |
||
|capacity=44 Passengers (Passenger configuration) |
|capacity=44 Passengers (Passenger configuration) |
||
|length ft=95 |
|||
|payload main= |
|||
| |
|length in=2 |
||
| |
|length note= |
||
|span ft=123 |
|||
|length main= 95 ft 2 in |
|||
|span in= |
|||
|length alt= 29.007 m |
|||
|span |
|span note= |
||
|height ft=22 |
|||
|span alt= 37.49 m |
|||
|height |
|height in=5 |
||
|height |
|height note= |
||
|area |
|wing area sqft=1650 |
||
|area |
|wing area note= |
||
|aspect ratio=<!-- sailplanes --> |
|||
|airfoil= |
|||
|airfoil='''root:''' [[NACA airfoil|NACA 23018]]; '''tip:''' [[NACA airfoil|NACA 4412]]<ref name="Selig">{{cite web |last1=Lednicer |first1=David |title=The Incomplete Guide to Airfoil Usage |url=https://m-selig.ae.illinois.edu/ads/aircraft.html |website=m-selig.ae.illinois.edu |access-date=16 April 2019}}</ref> |
|||
|aspect ratio= |
|||
|empty weight |
|empty weight lb=61235 |
||
|empty weight |
|empty weight note= |
||
| |
|gross weight lb= |
||
| |
|gross weight note= |
||
|max takeoff weight lb=107000 |
|||
|useful load main= |
|||
|max takeoff weight note= |
|||
|useful load alt= |
|||
|fuel capacity= |
|||
|max takeoff weight main= 107,000 lbs |
|||
|max takeoff weight alt= 48,534.4 kg |
|||
|more general= |
|more general= |
||
<!-- |
<!-- |
||
Powerplant |
Powerplant |
||
--> |
--> |
||
|eng1 number=4 |
|||
|engine (jet)= |
|||
|eng1 name=[[Wright R-3350-75 Duplex-Cyclone]] |
|||
|type of jet= |
|||
|eng1 type=18-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines |
|||
|number of jets= |
|||
|eng1 hp=2500 |
|||
|thrust main= |
|||
| |
|eng1 note= |
||
|thrust original= |
|||
|afterburning thrust main= |
|||
|afterburning thrust alt= |
|||
|engine (prop)= [[Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone|Wright R-3350-75]] |
|||
|type of prop=[[radial engine]]s |
|||
|number of props=4 |
|||
|power main= 2,500 bhp |
|||
|power alt= 1,866 kW |
|||
|power original= |
|||
|propeller or rotor?=propeller |
|||
|propellers=4 |
|||
|number of propellers per engine=1 |
|||
|propeller diameter main= |
|||
|propeller diameter alt= |
|||
<!-- |
|||
Performance |
|||
--> |
|||
|max speed main= 334 mph |
|||
|max speed alt= 537.52 km/h |
|||
|max speed more= |
|||
|cruise speed main= 324 mph |
|||
|cruise speed alt= 521.43 km/h |
|||
|cruise speed more= |
|||
|stall speed main= |
|||
|stall speed alt= |
|||
|stall speed more= |
|||
|never exceed speed main= |
|||
|never exceed speed alt= |
|||
|range main= |
|||
|range alt= |
|||
|range more= |
|||
|combat radius main= |
|||
|combat radius alt= |
|||
|combat radius more= |
|||
|ferry range main= |
|||
|ferry range alt= |
|||
|ferry range more= |
|||
|endurance= |
|||
|ceiling main= 24,442 ft |
|||
|ceiling alt= 7,450 m |
|||
|ceiling more= |
|||
|climb rate main= |
|||
|climb rate alt= |
|||
|climb rate more= |
|||
|sink rate main= |
|||
|sink rate alt= |
|||
|sink rate more= |
|||
|loading main= |
|||
|loading alt= |
|||
|thrust/weight= |
|||
|power/mass main= |
|||
|power/mass alt= |
|||
|more performance= |
|||
<!-- |
|||
Armament |
|||
--> |
|||
|armament=<!-- if you want to use the following specific parameters, do not use this line at all--> |
|||
|guns= |
|||
|bombs= |
|||
|rockets= |
|||
|missiles= |
|||
|hardpoints= |
|||
|hardpoint capacity= |
|||
|hardpoint rockets= |
|||
|hardpoint missiles= |
|||
|hardpoint bombs= |
|||
|hardpoint other= |
|||
|avionics= |
|||
|prop blade number=3 |
|||
}} |
|||
|prop name=constant-speed feathering propellers |
|||
|prop dia ft=<!-- propeller aircraft --> |
|||
===R7V-1/C-121J (L-1049B)=== |
|||
|prop dia in=<!-- propeller aircraft --> |
|||
|prop dia note= |
|||
[[File:Super Constellation Silh.jpg|thumb]] |
|||
{{aircraft specifications |
|||
<!-- if you do not understand how to use this template, please ask at [[Wikipedia talk:WikiProject Aircraft]] --> |
|||
|plane or copter?=plane |
|||
|jet or prop?=prop |
|||
<!-- Now, fill out the specs. Please include units where appropriate (main comes first, alt in parentheses). If an item doesn't apply, like capacity, leave it blank. |
|||
--> |
|||
|ref=''Lockheed Constellation:From Excalibur to Starliner''.<ref>Breffort, 2006</ref> |
|||
<!-- |
|||
General characteristics |
|||
--> |
|||
|crew=4 |
|||
|capacity=97-107 Passengers (Passenger configuration) |
|||
|payload main= |
|||
|payload alt= |
|||
|payload more= |
|||
|length main= 116 ft 2 in |
|||
|length alt= 35.408 m |
|||
|span main= 123 ft |
|||
|span alt= 37.49 m |
|||
|height main= 24 ft 9 in |
|||
|height alt= 7.5438 m |
|||
|area main= 1,650 sq ft |
|||
|area alt= 153.29 sq m |
|||
|airfoil= |
|||
|aspect ratio= |
|||
|empty weight main= 72,815 lbs |
|||
|empty weight alt= 33,028.3 kg |
|||
|loaded weight main= |
|||
|loaded weight alt= |
|||
|useful load main= |
|||
|useful load alt= |
|||
|max takeoff weight main= 145,000 lb |
|||
|max takeoff weight alt= 65,770.9 kg |
|||
|more general= |
|||
<!-- |
|||
Powerplant |
|||
--> |
|||
|engine (jet)= |
|||
|type of jet= |
|||
|number of jets= |
|||
|thrust main= |
|||
|thrust alt= |
|||
|thrust original= |
|||
|afterburning thrust main= |
|||
|afterburning thrust alt= |
|||
|engine (prop)= [[Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone|Wright R-3350-34]] |
|||
|type of prop=[[radial engine]]s |
|||
|number of props=4 |
|||
|power main= 3250 bhp |
|||
|power alt= 2,240 kW |
|||
|power original= |
|||
|propeller or rotor?=propeller |
|||
|propellers=4 |
|||
|number of propellers per engine=1 |
|||
|propeller diameter main= |
|||
|propeller diameter alt= |
|||
<!-- |
<!-- |
||
Performance |
Performance |
||
--> |
--> |
||
|max speed |
|max speed mph=334 |
||
|max speed |
|max speed note= |
||
| |
|cruise speed mph=324 |
||
|cruise speed |
|cruise speed note= |
||
| |
|stall speed mph= |
||
| |
|stall speed note= |
||
| |
|never exceed speed mph= |
||
| |
|never exceed speed note= |
||
| |
|minimum control speed mph= |
||
| |
|minimum control speed note= |
||
|range miles= |
|||
|never exceed speed alt= |
|||
|range |
|range note= |
||
|range |
|ferry range miles= |
||
|range |
|ferry range note= |
||
|endurance=<!-- if range unknown --> |
|||
|combat radius main= |
|||
|ceiling ft=24442 |
|||
|combat radius alt= |
|||
|ceiling note= |
|||
|combat radius more= |
|||
| |
|climb rate ftmin= |
||
| |
|climb rate note= |
||
|time to altitude= |
|||
|ferry range more= |
|||
|lift to drag= |
|||
|endurance= |
|||
|wing loading lb/sqft= |
|||
|ceiling main= 24,442 ft |
|||
|wing loading note= |
|||
|ceiling alt= 7,449 m |
|||
|fuel consumption lb/mi= |
|||
|ceiling more= |
|||
|power/mass= |
|||
|climb rate main= |
|||
|more performance=<!--</br> |
|||
|climb rate alt= |
|||
*'''Take-off run:''' {{cvt||ft|0}} |
|||
|climb rate more= |
|||
*'''Take-off distance to {{cvt|50|ft|0}}:''' {{cvt||ft|0}} |
|||
|sink rate main= |
|||
*'''Landing run:''' {{cvt||ft|0}} |
|||
|sink rate alt= |
|||
*'''Landing distance from {{cvt|50|ft|0}}:''' {{cvt||ft|0}}--> |
|||
|sink rate more= |
|||
|loading main= |
|||
|loading alt= |
|||
|thrust/weight= |
|||
|power/mass main= |
|||
|power/mass alt= |
|||
|more performance= |
|||
<!-- |
|||
Armament |
|||
--> |
|||
|armament=<!-- if you want to use the following specific parameters, do not use this line at all--> |
|||
|guns= |
|||
|bombs= |
|||
|rockets= |
|||
|missiles= |
|||
|hardpoints= |
|||
|hardpoint capacity= |
|||
|hardpoint rockets= |
|||
|hardpoint missiles= |
|||
|hardpoint bombs= |
|||
|hardpoint other= |
|||
|avionics= |
|avionics= |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 329: | Line 188: | ||
<!-- include as many lines as are appropriate. additional lines/entries with a carriage return. --> |
<!-- include as many lines as are appropriate. additional lines/entries with a carriage return. --> |
||
|related= |
|related= |
||
* [[Lockheed C-69 Constellation]] |
|||
* [[Lockheed Constellation]] |
* [[Lockheed Constellation]] |
||
* [[Lockheed EC-121 Warning Star]] |
|||
* [[Lockheed L-049 Constellation]] |
* [[Lockheed L-049 Constellation]] |
||
* [[Lockheed C-69 Constellation]] |
|||
* [[Lockheed L-649 Constellation]] |
* [[Lockheed L-649 Constellation]] |
||
* [[Lockheed L-749 Constellation]] |
* [[Lockheed L-749 Constellation]] |
||
* [[Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation]] |
* [[Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation]] |
||
* [[Lockheed EC-121 Warning Star]] |
|||
* [[Lockheed L-1249 Super Constellation]] (R7V-2/YC-121F) |
* [[Lockheed L-1249 Super Constellation]] (R7V-2/YC-121F) |
||
* [[Lockheed L-1649 Starliner]] |
* [[Lockheed L-1649 Starliner]] |
||
|similar aircraft= |
|similar aircraft= |
||
* [[Boeing 377 Stratocruiser]] |
|||
* [[Boeing C-97 Stratofreighter]] |
* [[Boeing C-97 Stratofreighter]] |
||
* [[Boeing KC-97 Stratofreighter]] |
* [[Boeing KC-97 Stratofreighter]] |
||
* [[Boeing 377]] |
|||
* [[Bristol Britannia]] |
* [[Bristol Britannia]] |
||
* [[Canadair CC-109 Cosmopolitan]] |
|||
* [[Convair C-131 Samaritan]] |
* [[Convair C-131 Samaritan]] |
||
* [[Canadair CC-109 Cosmopolitan]] |
|||
* [[Douglas C-54 Skymaster]] |
* [[Douglas C-54 Skymaster]] |
||
* [[Douglas DC-6|Douglas DC-6/C-118 Liftmaster]] |
* [[Douglas DC-6|Douglas DC-6/C-118 Liftmaster]] |
||
| Line 351: | Line 210: | ||
|lists= |
|lists= |
||
* [[List of Lockheed aircraft]] |
* [[List of Lockheed aircraft]] |
||
* [[List of models of the Lockheed Constellation]] |
|||
* [[List of Lockheed Constellation operators]] |
* [[List of Lockheed Constellation operators]] |
||
* [[Lockheed Constellation variants]] |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 362: | Line 221: | ||
===Bibliography=== |
===Bibliography=== |
||
{{refbegin}} |
{{refbegin}} |
||
*Breffort, Dominique. ''Lockheed Constellation: from Excalibur to Starliner Civilian and Military Variants''. Paris: Histoire and Collecions, 2006. Print. ISBN |
*Breffort, Dominique. ''Lockheed Constellation: from Excalibur to Starliner Civilian and Military Variants''. Paris: Histoire and Collecions, 2006. Print. {{ISBN|2-915239-62-2}}. |
||
*Winchester, Jim. ''Lockheed Constellation'' (Classic Airliners). St Paul, MN:MBI Publishing 2001. ISBN |
*Winchester, Jim. ''Lockheed Constellation'' (Classic Airliners). St Paul, MN:MBI Publishing 2001. {{ISBN|0-7603-1198-6}}. |
||
{{refend}} |
{{refend}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Commons |
{{Commons category}} |
||
* [http://www.conniesurvivors.com/ Lockheed Constellation Survivors] - A website that explains information and whereabouts of surviving Constellations of all variants, including the Super Constellation. |
* [http://www.conniesurvivors.com/ Lockheed Constellation Survivors] - A website that explains information and whereabouts of surviving Constellations of all variants, including the Super Constellation. |
||
| Line 374: | Line 233: | ||
{{USAF transports}} |
{{USAF transports}} |
||
{{USN transports}} |
{{USN transports}} |
||
{{USAF system codes}} |
|||
[[Category:Lockheed aircraft|C-121]] |
[[Category:Lockheed aircraft|C-121]] |
||
[[Category:United States military transport aircraft |
[[Category:1950s United States military transport aircraft]] |
||
[[Category:Four-engined tractor aircraft]] |
[[Category:Four-engined tractor aircraft]] |
||
[[Category:Low-wing aircraft]] |
[[Category:Low-wing aircraft]] |
||
[[Category:Lockheed Constellation|C-121]] |
[[Category:Lockheed Constellation|C-121]] |
||
[[Category:Articles containing video clips]] |
[[Category:Articles containing video clips]] |
||
[[Category:Aircraft first flown in 1947]] |
|||
[[Category:Four-engined piston aircraft]] |
|||
[[Category:Triple-tail aircraft]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 02:22, 21 April 2024
| C-121/R7O/R7V Constellation | |
|---|---|

| |
| A Military Air Transport Service C-121G Super Constellation flying near the Golden Gate Bridge. | |
| Role | Military transport |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Lockheed Corporation |
| First flight | March 14, 1947 |
| Introduction | November 12, 1948 |
| Status | Retired from military service, two operated by civilian preservation organisations |
| Primary user | United States Air Force United States Navy |
| Produced | 1947 to 1958 |
| Number built | 332 |
| Developed from | L-749 Constellation L-1049 Super Constellation |
| Variants | R7V-2/YC-121F Constellation EC-121 Warning Star |
The Lockheed C-121 Constellation is a military transport version of the Lockheed Constellation. A total of 332 aircraft were constructed for both the United States Air Force and United States Navy for various purposes. Numerous airborne early warning versions were also constructed. The C-121 later saw service with smaller civilian operators until 1993.
Design and development[edit]


Lockheed's first attempt at a military version of the Constellation airliner had been unsuccessful. This was largely due to the problems encountered by the Wright R-3350 engines that powered the aircraft. After the war, the few military Constellations built (designated C-69) were retrofitted by Lockheed for use in the post-war airline industry as the L-049.
In 1947, Lockheed unveiled a more economical Constellation. The L-749 as it was known, had extra fuel capacity and a more economical version of the R-3350. However, Lockheed had lost 1200 workers that same year. By 1948, production of the L-749 was at a near halt. It was then that the United States Air Force (USAF) signed a contract with Lockheed for ten L-749A aircraft designated the C-121A. The United States Navy (USN) had also placed an order for two AWACS versions of the L-749A designated the PO-1W (later WV-1). The first L-749A variants off the production line were for the US military.
The C-121A versions differed from the L-749 only through having a reinforced floor to handle cargo, and a large aft loading door. Although originally intended for cargo transport duties, they were usually fitted out with 44-seat passenger transport interiors. The aircraft also consisted of a five-man crew with four relief crew members on standby. All C-121As were assigned to the Atlantic division of the Military Air Transport Service (MATS). The aircraft would later see service in the Berlin Airlift. Dwight Eisenhower and General Douglas MacArthur both used the C-121A as their personal VIP transports. In 1950, six of the C-121A Constellations were modified as VIP transports and redesignated VC-121A. The last C-121As were retired in 1968.
In August 1950, the USN ordered eleven passenger/cargo convertible versions of Lockheed's stretched L-1049B Super Constellation (which it had already ordered as the WV-2 AWACS platform). These aircraft, originally designated R7O, were delivered before the WV-2 aircraft due to the R7O being more simple to produce. The R7O (now R7V-1) first flew in 1952. The R7V-1 was able to be quickly converted between a passenger transport for 97-107 individuals or a cargo carrying transport in two hours. The Navy reduced the number of available seats to fit room for life rafts on overseas flights. 73 stretchers could also be used for medical evacuation flights. The R7V-1s saw service over the Atlantic and Pacific in squadrons VR-1 (the oldest transport squadron in the Navy), VR-7 and VR-8. Two modified R7V-1 aircraft were used on Antarctic supply missions while conducting tests and observations at the same time. One crashed on landing in 1970 and remains at the spot to the present day; the other was retired in 1971. In 1962, 32 of the 50 R7V-1 aircraft in Naval service were transferred to the Air Force, being re-designated the C-121G. The remaining 18 in Naval service were redesignated C-121J. One C-121J was later used by the Blue Angels until it was replaced by a Lockheed C-130 Hercules in 1971.

The USAF had also ordered 33 L-1049F Super Constellations in 1951, designated the C-121C. Unlike its Naval equivalent, the C-121C featured square cabin windows instead of round ones. Otherwise, the C-121C resembled the USN R7V-1 aircraft. The C-121C also featured a reinforced structure to handle turboprop engines if necessary. Other features of the C-121C included an Auxiliary Power Unit, Turbo-compound R-3350s, and the ability to carry 75 passengers, 72 fully equipped troops, or 47 stretchers. The seats could be stored under the floor of the aircraft when needed for cargo use. The first flight of a C-121C was in 1955. Deliveries began in August 1955, with aircraft being assigned to the MATS Atlantic division. The aircraft were later in service with the Air National Guard (ANG) and were retired in 1973. Four were later refitted as VC-121C VIP aircraft, six as EC-121S TV and radio broadcast relay systems, two became EC-121C Microwave Airborne Radio Communications (MARCOM) systems and one was converted to a DC-121C observation aircraft.
After military service, some C-121s and R7V-1s were used by civilian operators as cargo aircraft. The last operators were small Dominican Republic cargo airlines that operated to Miami with surplus military Constellations bought from Davis-Monthan Air Force Base. The operations stopped in 1993 after the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) banned these operators from flying into the United States due to safety concerns. One former C-121Cs fly today with the Historical Aircraft Restoration Society of Australia and the other flew up to 2016 to Super Constellation Flyers Association of Switzerland.[1][2] The DIAG Aviation GmbH with the until 2016 flown exemplar is since then dismounted and put to be sold from 5 April 2023.[3]
Variants[edit]
Air Force[edit]
- C-121A
- Initial variant, based on the civil L-749 Constellation. Nine built.
- VC-121A
- Six C-121A transports converted to VIP use. Originally designated PC-121A.
- VC-121B
- Similar to the VC-121A, but with the cargo door replaced by a smaller passenger door. One built.
- C-121C
- Initial variant based on the L-1049 Super Constellation. 33 built.
- VC-121C
- VIP conversion of four C-121C aircraft.

- VC-121E
- Ordered by the United States Navy as a R7V-1 but modified before delivery as a presidential transport for the United States Air Force.
- YC-121F
- Two former United States Navy R7V-2s with Pratt & Whitney T34 turboprop engines transferred to the United States Air Force. Designated L-1249A by Lockheed.[4]
- C-121G
- Redesignation of 32 R7V-1 transports transferred from the USN to the Air Force.
- TC-121G
- Three C-121Gs converted to AWACS crew trainers.
- VC-121G
- One C-121G converted to a VIP transport.
[edit]
- R7V-1
- Initial Navy version based on the L-1049. 50 built. Originally designated R7O.
- R7V-1P
- One R7V-1 modified for Antarctic service.
- R7V-2
- Two transport aircraft similar to the YC-121F. Also designated L-1249A. Two built.
- C-121J
- 18 remaining R7V-1s redesignated.
- TC-121J
- Electronic testbed. One converted.
- NC-121J
- Four C-121J aircraft converted to television broadcasting aircraft for use in Vietnam. Project Jenny ( Blue Eagles ) VXN-8
- VC-121J
- Four C-121J aircraft converted for VIP use. One operated with the Blue Angels.
Surviving aircraft[edit]
- N422NA - C-121A - Airworthy[6]
- 54-0177 - C-121C on static display at the Smithsonian Institution's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Virginia[7]
Specifications (C-121A / L-749A)[edit]
Data from Lockheed Constellation:From Excalibur to Starliner,[8] Lockheed Constellation:From Excalibur to Starliner[9]
General characteristics
- Crew: 5
- Capacity: 44 Passengers (Passenger configuration)
- Length: 95 ft 2 in (29.01 m)
- Wingspan: 123 ft (37 m)
- Height: 22 ft 5 in (6.83 m)
- Wing area: 1,650 sq ft (153 m2)
- Airfoil: root: NACA 23018; tip: NACA 4412[10]
- Empty weight: 61,235 lb (27,776 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 107,000 lb (48,534 kg)
- Powerplant: 4 × Wright R-3350-75 Duplex-Cyclone 18-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 2,500 hp (1,900 kW) each
- Propellers: 3-bladed constant-speed feathering propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 334 mph (538 km/h, 290 kn)
- Cruise speed: 324 mph (521 km/h, 282 kn)
- Service ceiling: 24,442 ft (7,450 m)
See also[edit]
Related development
- Lockheed C-69 Constellation
- Lockheed Constellation
- Lockheed EC-121 Warning Star
- Lockheed L-049 Constellation
- Lockheed L-649 Constellation
- Lockheed L-749 Constellation
- Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation
- Lockheed L-1249 Super Constellation (R7V-2/YC-121F)
- Lockheed L-1649 Starliner
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- Boeing 377 Stratocruiser
- Boeing C-97 Stratofreighter
- Boeing KC-97 Stratofreighter
- Bristol Britannia
- Canadair CC-109 Cosmopolitan
- Convair C-131 Samaritan
- Douglas C-54 Skymaster
- Douglas DC-6/C-118 Liftmaster
- Douglas DC-7
- Ilyushin Il-18
Related lists
References[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ L1049 Super Constellation - Lockheed Constellation Survivors; Petersen, Ralph M.; Retrieved 8/4/11
- ^ Breffort, 2006, pp.146-159.
- ^ "Um dos dois últimos Lockheed Constellation C-121C do mundo pode nunca mais voar". 7 April 2023.
- ^ a b C-69/C-121 - US Warplanes.net Archived 2015-10-26 at the Wayback Machine; Retrieved 11/6/11
- ^ Breffort, 2006, pp.166-169.
- ^ "C-121A Constellation". Lewis Air Legends. Retrieved 2023-05-08.
- ^ "Lockheed 1049F-55-96, "Constellation"". National Air and Space Museum. 1943-01-09. Retrieved 2024-04-21.
- ^ Breffort, 2006, p.175.
- ^ Breffort, 2006
- ^ Lednicer, David. "The Incomplete Guide to Airfoil Usage". m-selig.ae.illinois.edu. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
Bibliography[edit]
- Breffort, Dominique. Lockheed Constellation: from Excalibur to Starliner Civilian and Military Variants. Paris: Histoire and Collecions, 2006. Print. ISBN 2-915239-62-2.
- Winchester, Jim. Lockheed Constellation (Classic Airliners). St Paul, MN:MBI Publishing 2001. ISBN 0-7603-1198-6.
External links[edit]
- Lockheed Constellation Survivors - A website that explains information and whereabouts of surviving Constellations of all variants, including the Super Constellation.